By: Shreya Srinivas
In today’s technology industry, we see and hear a lot about these “buzz” words like AI, ML, GenAI and LLM .So, I would like to give a distinguishing difference about what each of these technologies mean and how they differ from each other.
Here is a small pictorial representation of the same:
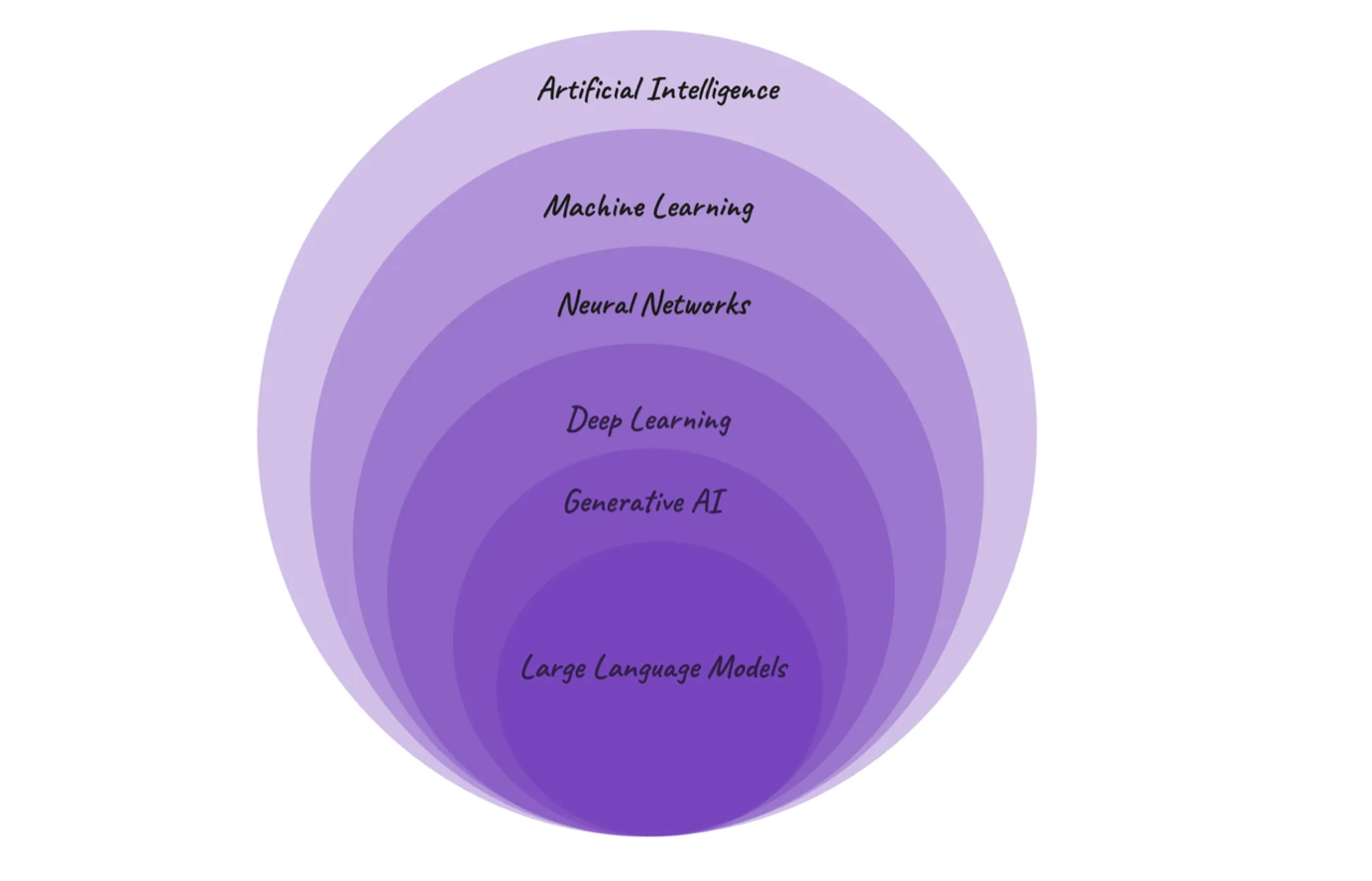
What is AI?
AI, or artificial intelligence, refers to the mechanism of making computers or any machine intelligent enough to perform tasks that usually require humans. Artificial intelligence serves as a broad umbrella under which multiple technologies are present.
What is ML?
Machine learning is a branch of AI that deals with multiple algorithms and uses the available data to replicate the way humans perform particular tasks. As the machine gradually learns a task and improves accuracy through multiple runs/executions it is aptly called machine learning. The logic used to learn and execute the task differs with different algorithms. There are multiple algorithms available, each suitable for different use cases. A programmer writing ML code can use existing algorithms or write and code new algorithms tailored to their use case. Machine learning programs are called models, and they require to be trained before being applied in a use case.
By training, we mean that a person who developed the model needs to provide some data to the model and make it learn how to use the data to serve the purpose it was built for. The more varied types of data the model is exposed to during training, the more accurate the results of the ML model will be. Therefore, training an ML model is a very important step before using it in a real-life use case.
What is deep learning?
DDeep learning is a type of machine learning algorithm that replicates the complex decision-making of the human brain and uses neural networks to do so.
What is GenAI?
GenAI is a type of artificial intelligence platform which uses ML models to generate new content in response to certain input prompts. The content can be text, images, video, or audio. These outputs are generated based on training data, and the responses are a combination of deep learning and neural network algorithms to make the responses more accurate, capable of recognizing patterns, and adapt accordingly to new input prompts.
What is a Large Language Model?
Large language models are a subtype of generative AI platforms. They are huge machine learning models that can converse like humans in normal language. They are intelligent enough to replicate human conversations by reading input in normal language and generating output in normal human language. Internally, these models use deep learning techniques, neural networks, and analysis of large training data to generate accurate and apt responses like a human to a user.
So, the above classification can be summarized as :
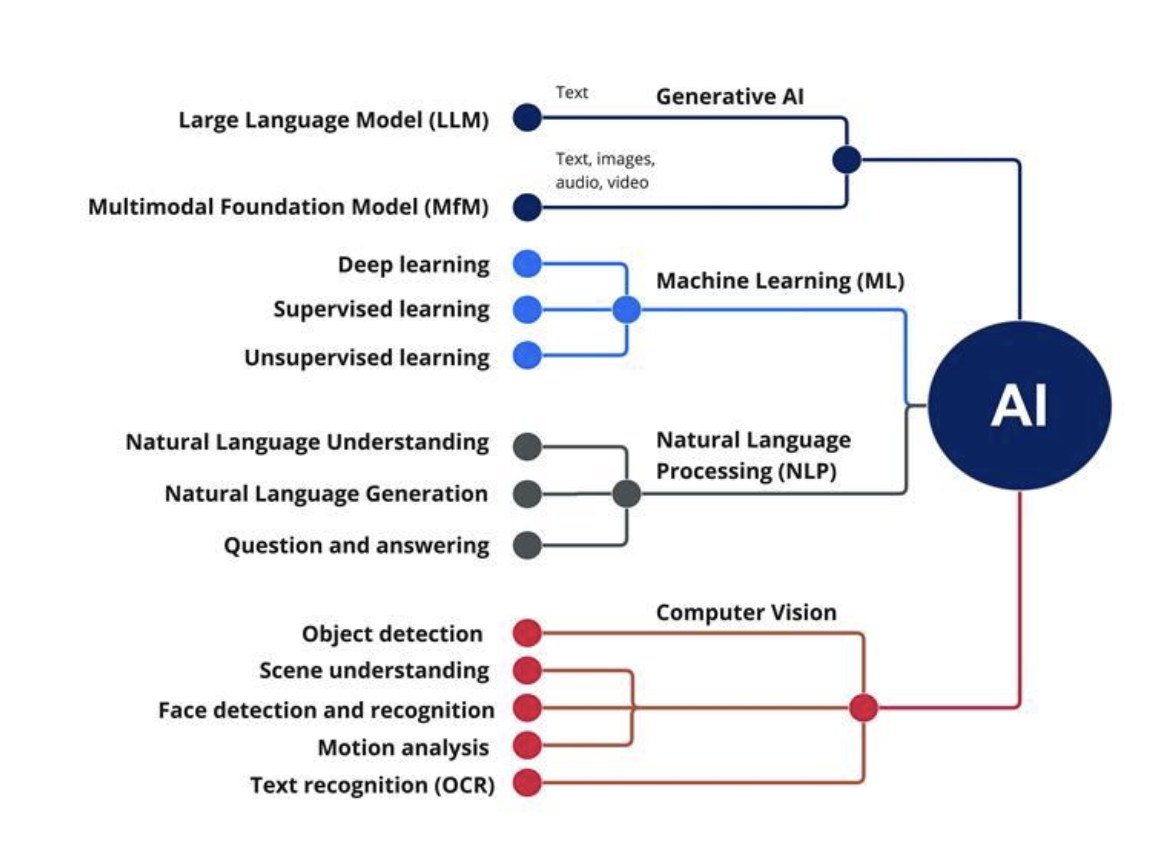
Use cases in the tech industry:
- IT support and helpdesk automation: This implementation is already visible in many organizations where the first level of tech support or helpdesk is replaced by automated chatbots capable of efficiently answering most expected queries from users.
- Data analytics and business intelligence: With AI-based applications, deeper and more accurate data analytics is possible. Using predictive analytics, data forecasting can be done to identify customer behavioural, market, and operational changes according to the situation. Using prescriptive analytics, strategies can be identified to cater to the anticipated changes. Using NLP, even a non-technical person could request BI reports to be generated, receiving insights in a conversational manner (as good as talking to your team and getting a particular report generated, but this is automated and can be customized according to needs on the fly).
- Software Development: We can have AI based applications read our code base and identify patterns and enable some base level review parameters, hence automating the code review process in development teams. We could also have LLMs to help with code debugging and suggest fixes on the fly in our coding environments.
- IT asset management: We can have AI models to identify patterns among the company assets and predict if any maintenance is needed on these machines based on utilisation patterns. This will help to maintain compliance and updated inventory details in turn reducing over or under utilisation of resources and leading to reduced company costs.
- IT operations: In ops teams, we can automate menial routine tasks using AI and use AI analytical algorithms to continuously analyse data from different sources and logs of different platforms in order to auto-fix most frequently occurred issues or predict any new issues that might occur due to logs errors or resource overloading etc. AI can also be used for performance analysis and adjusting resources based on the workload on the system. These actions free human resources to concentrate more on strategic improvements in the infrastructure rather than repeatedly performing routine maintenance tasks.
Is AI really going to replace Software professionals?
Looking at the above use cases, one might think, if machines are capable of doing these things, then why do we need software professionals to do the same? The above use cases are only capable of performing what they are coded to perform. We will always need software professionals to improve and maintain these models/machines. AI and ML are tools that help the software industry become more intelligent and move ahead with advanced technologies, eliminating human intervention only for routine tasks. They also help make the development/ops process faster and deliver better quality products than ever before. So, in conclusion, there is no danger to software professionals due to AI; rather, it’s a huge leap forward in the technology world to help deliver some great products of good value, great impact, and high quality.





