By: Anant Govil
Introduction : At the Crossroads of Innovation and Security
In an era where digital innovation unfolds at breakneck speed, the emergence of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) stands as a testament to human ingenuity. With McKinsey Global Institute estimating that GenAI could contribute an astounding $2.6 to $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy, potentially increasing AI's economic impact by 15% to 40%. Yet, this bright horizon is not without its dark clouds, particularly in the realm of cybersecurity.
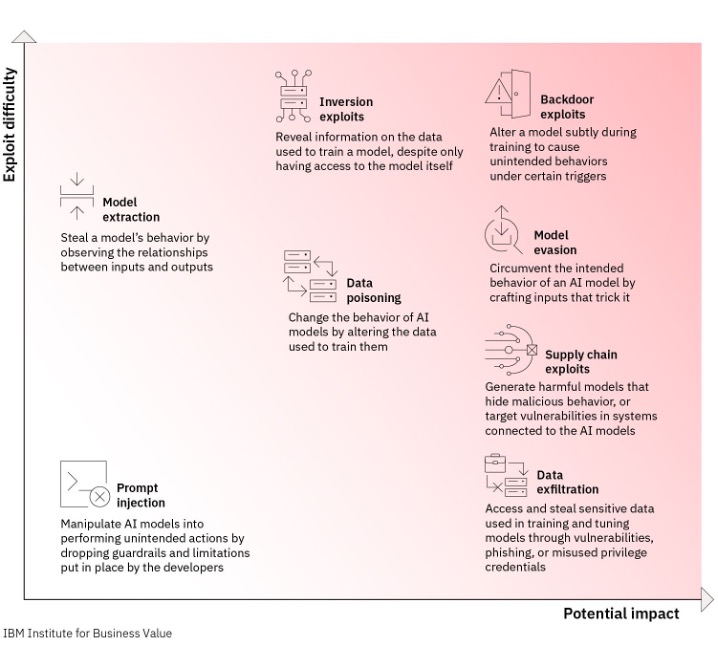
The Cybersecurity Conundrum
As we marvel at the pace of digital innovation, a shadow looms large: cybersecurity risks. The advent of GenAI has provided cybercriminals with powerful tools to escalate their attacks, making them more sophisticated and successful. From crafting highly convincing phishing attempts to enhancing ransomware effectiveness, modern hackers are leveraging AI to transform the cybersecurity landscape.
The stakes are high, with worldwide cybercrime costs projected to soar to $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, according to Cybersecurity Ventures. This alarming figure underscores the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard our digital future.
The Innovation-Security Paradox
As organizations rush to create value from generative AI, many are speeding past a critical element: security.
A study by the IBM Institute for Business Value reveals a startling disconnect; while 82% of C-suite executives acknowledge the importance of secure and trustworthy AI, only 24% of gen AI projects include a security component. This oversight is particularly concerning given the executives' awareness of the significant security vulnerabilities associated with gen AI.

The Rising Tide of AI-Driven Threats
The proliferation of SaaS applications, fueled by the rapid adoption of AI technologies, has opened new avenues for threat actors.
The meteoric rise of platforms like ChatGPT, which reached one million users in just five days, exemplifies the growing appeal of AI applications. This surge in popularity, however, also amplifies the risk of breaches, making AI applications prime targets for cybercriminals.
The Path Forward: Leveraging AI for Enhanced Cybersecurity
In the face of escalating cyber threats, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in fortifying cybersecurity frameworks has never been more critical. AI's prowess in pattern recognition and anomaly detection offers a beacon of hope, providing a sophisticated shield against the complexities of cyber-attacks. This section delves into the transformative potential of AI in detecting and preventing cybersecurity vulnerabilities, underscoring its indispensability in the digital age.
AI in Anomaly Detection: A Game-Changer
AI's capability to discern patterns and identify deviations from the norm makes it an invaluable asset in cybersecurity. Through machine learning, AI models are trained to understand what constitutes normal behaviour within a system, enabling them to detect anomalies that could signify potential attacks or system malfunctions. This approach is not limited to network traffic or user activities; it extends to monitoring organizational data for signs of cyber threats on a global scale.
-
Use Case 1: Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting
AI excels in real-time monitoring of system behaviours, from network traffic to API calls, employing statistical analysis to identify and alert on anomalous activities. This capability is crucial in preventing "alert fatigue" by prioritizing events and enabling informed decision-making, thus enhancing the overall security posture.
-
Use Case 2 : AI-Assisted Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
Beyond detection, AI plays a pivotal role in cyber threat intelligence, gathering and analysing data on cyber-attacks to inform and prepare organizations proactively. By automating routine tasks, AI allows security teams to concentrate on strategic decision-making, bolstering defences before threats materialize.
Preventing Vulnerabilities with AI
AI's contribution to cybersecurity extends to the prevention of software vulnerabilities. AI-assisted tools in code editors and build pipelines are revolutionizing the way code is reviewed and tested, reducing the incidence of false positives and enhancing the efficiency of security testing.
-
Use Case 3: AI-Assisted Code Scanning
AI's integration into Static Application Security Testing (SAST) and Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools is transforming code scanning and application testing. By understanding the context of potential security issues, AI reduces false positives and aids developers in identifying errors early in the development process.
-
Use Case 4: Automated Vulnerability Discovery
AI's application in DAST tools streamlines the testing of running applications against common attacks, significantly reducing the need for extensive penetration testing. This automation not only saves time and resources but also enhances the effectiveness of security measures.
Protecting AI Itself
As AI becomes increasingly integrated into cybersecurity strategies, ensuring the security of AI systems themselves is paramount. Addressing challenges such as data poisoning, model validation, and system transparency is essential to prevent AI from becoming a liability. Moreover, as regulatory frameworks around AI evolve, prioritizing the security and validity of AI systems will be crucial for compliance and effectiveness.
Final thoughts
The integration of AI into cybersecurity represents a significant leap forward in the battle against cyber threats. By harnessing AI for anomaly detection, cyber threat intelligence, and vulnerability prevention, organizations can significantly enhance their defensive capabilities. However, as we leverage AI's potential, we must also be vigilant in securing AI systems against exploitation. The path forward is clear: embracing AI in cybersecurity is not just an option; it's a necessity for safeguarding our digital future in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
REFERENCES
- https://www.ibm.com/thought-leadership/institute-business-value/report/securing-generative-ai
- https://futurecio.tech/a-cisos-guide-to-the-role-of-ai-in-cybersecurity/
- https://wing.security/resources/blog/saas-security/what-you-need-to-know-about-ai-and-saas-cybersecurity/





