By: Chandan Patro

Software as a Service (SaaS) business model represents how software is delivered, accessed, and monetized, and it has revolutionized the way software is delivered and consumed.
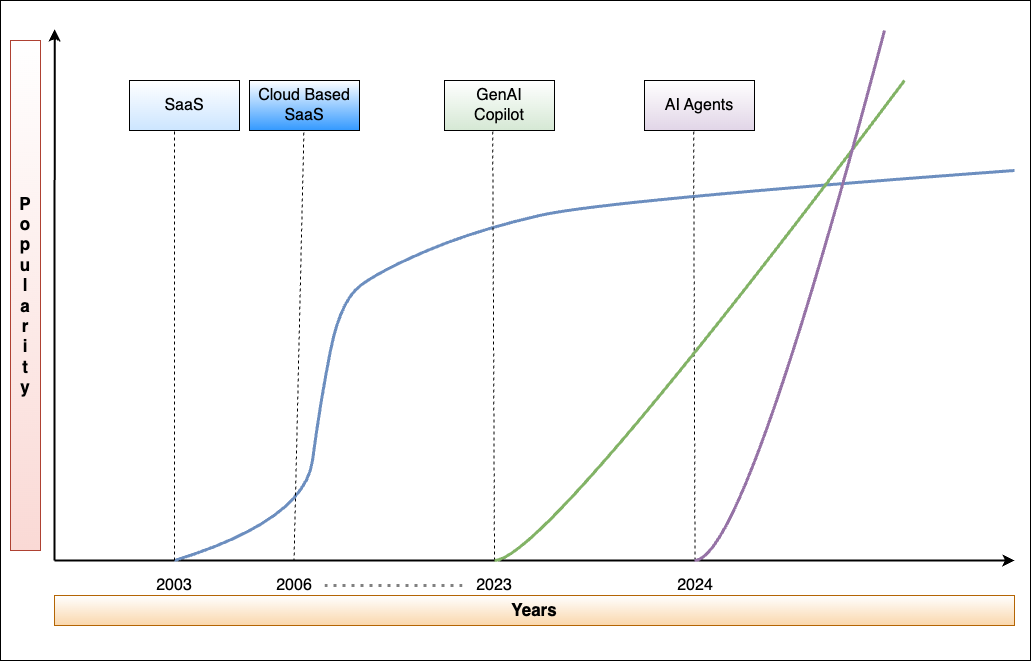
The early 2000s marked the true birth of the SaaS model, catalyzed by the increasing availability of broadband internet and improvements in web technologies. It represents a shift from traditional software purchase and installation on individual computers or servers, to a subscription-based model where software is hosted in the cloud and accessed via the internet.
SaaS models have undergone significant evolution over the last two decades, propelled by advancements in cloud computing, data analytics, and artificial intelligence; and are characterized by key components:
- Subscription-Based Pricing: Customers pay a recurring fee, often monthly or annually, to access the software.
- Centralized Hosting: Software applications are hosted on the provider's servers, allowing for centralized updates, maintenance, and security measures.
- Scalability: Customers can easily scale their usage up or down based on their needs, without the need for significant hardware investments.
- Accessibility: Being internet-based, SaaS applications can be accessed from anywhere, at any time, and on any device with internet connectivity.
- Automatic Updates: Providers can roll out updates and new features seamlessly to all users, ensuring that customers always have access to the latest version of the software.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) involves integrating intelligent algorithms and machine learning capabilities into cloud-based software applications. Gen-AI is a comprehensive field encompassing a wide array of AI systems. It has already proven to be a disruptor in the IT industry and holds the potential for a software framework wherein Gen-AI and humans operate simultaneously to produce customized software solutions. These AI-based agents might result in a complete overhaul of traditional SaaS-based solutions. An AI Agent is a system designed to perceive, make decisions, and perform actions to achieve specific goals. It can operate autonomously, functioning independently without direct intervention.
Internal working of an AI Agent:
- Goal Comprehension: To correctly understand a task, it might generate a preliminary response, often leveraging insights from a core large language model.
- Task List Creation: The agent formulates a list of tasks that align with the objective.
- Information Gathering: The agent ingests information, which includes navigating the web and along with other AI models for specialized tasks, ensuring a comprehensive approach to data collection.
- Data Management and Strategy Refinement: The agent continuously refines its approach based on ongoing communication with the user and feedback received.
- Continuous Iteration and Evaluation: The agent is in a constant state of iteration, where it evaluates its progress towards the goal by considering both external feedback and its internal analysis.
Types of AI Agent:
- Simple Reflex: These agents act based on the current state of their environment, using condition-action rules.
- Model-Based Reflex: These agents are more sophisticated than simple reflex agents, capable of dealing with partially observable environments.
- Goal-Based: These agents take actions based on achieving defined goals.
- Utility-Based: These agents evaluate actions based on a utility function, which assesses the desirability of outcomes.
- Learning: These agents are characterized by their ability to improve performance over time through learning.

AI Agents in SaaS
AI agents are ushering in a new era of smarter, more adaptable, and tailored software solutions within the Software as a Service (SaaS) sector, thanks to the latest developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning. Their integration into SaaS platforms is enhancing user experiences, streamlining processes through automation, and delivering insights based on data analysis.
- Personalization and User Experience - AI agents can analyze user behavior, preferences, and interactions within a SaaS application to deliver personalized content, recommendations, and features.
- Automation of Routine Tasks - AI agents can significantly increase efficiency and reduce the workload on human employees.
- Predictive Analytics and Insights - Leveraging large datasets, AI agents can provide predictive analytics, offering foresights into trends, user behavior, and potential system improvements.
- Enhanced Security - By continuously monitoring AI Agents can bolster the security of SaaS platforms to identify unusual patterns or behaviors indicative of security threats.
- Optimization of Resources - AI agents can dynamically adjust resources based on demand, optimizing data storage, and reducing operational costs.
- Intelligent Customer Support - AI agents can provide round the clock support improving customer satisfaction.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement - With continuous analysis of data and interactions, these agents can evolve to enhance the overall functionality and performance of the SaaS platform.
Inference
The idea of transitioning from specific, purpose-designed applications to more unified, intelligent agents mark a profound change in our technological interactions. In this envisioned future, some of the key aspects and consequences would include:
- Seamless Integration via NLP: The capacity to interact with AI using simple, everyday language, and having it comprehend the nuances of your life, represents a major advancement in user interface design. This indicates a future where technology becomes much more approachable for individuals, irrespective of their technical abilities, potentially narrowing the gap in digital literacy.
- Nuanced Personalization: The proposed AI agents, equipped with profound understanding of users' online and offline behaviors, offer a degree of customization previously unimaginable. This has the potential to transform service delivery, enabling everything from content suggestions to productivity aids to be customized according to everyone’s unique habits, tastes, and requirements.
- Breakthrough in Multimodal Capabilities: Versatile Multimodal Large Language Model underscores a major leap in AI functionalities.
- Emphasis on Privacy and Autonomy: It's vital that users have the power to regulate the extent of their data that AI can access and utilize.
- Transformation of Software Development and Usage: The shift would create a more dynamic and cost-efficient scenario for both consumers and creators.
While the potential benefits are significant, there are also challenges to consider, including:
- Privacy & Ethical Considerations: Monitoring both online behaviors and real-world actions brings up substantial privacy issues. The effectiveness of this approach depends on carefully balancing the need for personalized experiences with the protection of user privacy, guaranteeing that individuals retain complete authority over their information and its application. This situation will probably require the development of new privacy guidelines and potentially new laws to safeguard users.
- Inclusivity: Ensuring that these technologies are available to all individuals, regardless of their technical expertise or economic status.
- Equity and Impartiality: Tackling biases within AI models to promote fair and equal treatment across all user demographics.
Conclusion

As AI models advance, agents are poised to tackle more complex tasks, broadening their utility. Leveraging large language model (LLM) reasoning, their capacity to meet intricate objectives grows. The crucial factor is the ongoing refinement of these models to boost the AI agents' comprehension and ability to solve problems and are signaling a significant shift in the industry landscape, challenging the long-standing dominance of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies.
Technologies like NEXT-GPT and Similar Technologies represent a pivotal advancement in making this vision a reality. By processing and generating content across multiple modalities, these AI models can understand and produce a wide range of outputs, making interactions more natural and intuitive. This multimodal approach could also make technology more inclusive, catering to different learning and communication styles.
This would further enable personnel with no significant coding skills to generate customized solutions to solve problems and innovate. This could lead to a surge in creativity and a diversification of the types of applications and services available and could democratize software development.
Customized AI based niche solution could challenge the app-centric models and possibly reducing the dominance of major platforms. It could also change the nature of software development, shifting the focus towards designing sophisticated AI models rather than traditional app development, thereby democratizing software development.
Companies, which have been at the forefront of technological disruption for the past decade and have enjoyed high valuations based on the expectation of steadily increasing subscription revenues, may face a new reality as generative AI gains traction.





