By: Ananya Dixit
The history of language models has seen rapid development marked by notable breakthroughs in recent years. Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a paradigm shift in Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities, and they are the result of this evolutionary journey within the field of language processing.
The journey starts with primitive language models that served as the foundation for further advancements. Initially, language models were narrowly focused and found it difficult to represent the intricacies of spoken language. As technology capabilities increased, these models became more complex. Early versions produced text using statistical techniques and fundamental language norms, but they had issues with coherence and context.
Advances in natural language processing (NLP) and deep learning algorithms are driving the extraordinary expansion of the global large language model (LLM) market. Market forecasts indicate that the LLM market will expand at an astounding 40.7% CAGR, making it worth USD 6.5 billion by the end of 2024 and projected to reach USD 140.8 billion by 2033. The reason for this increase in demand is the extensive use of LLMs in a variety of industries and their revolutionary effect on jobs related to language generation, understanding, and prediction.
This growth rate of large language models can be attributed to the rapidly escalating requirements for advanced natural language processing capabilities across a wide range of industries. As businesses and organizations grapple with the ever-increasing volume of unstructured data, the need for robust language understanding and generation solutions has become paramount. LLMs, with their remarkable ability to comprehend and generate human-like text, offer a compelling solution to this challenge. From customer service and content creation to data analysis and decision support, the applications of LLMs span numerous sectors, including healthcare, finance, retail, and beyond. This demand, coupled with the continuous advancements in computational power and the availability of vast language data, has propelled the growth rate of LLMs, positioning them as a critical technology for unlocking the full potential of natural language processing across industries.
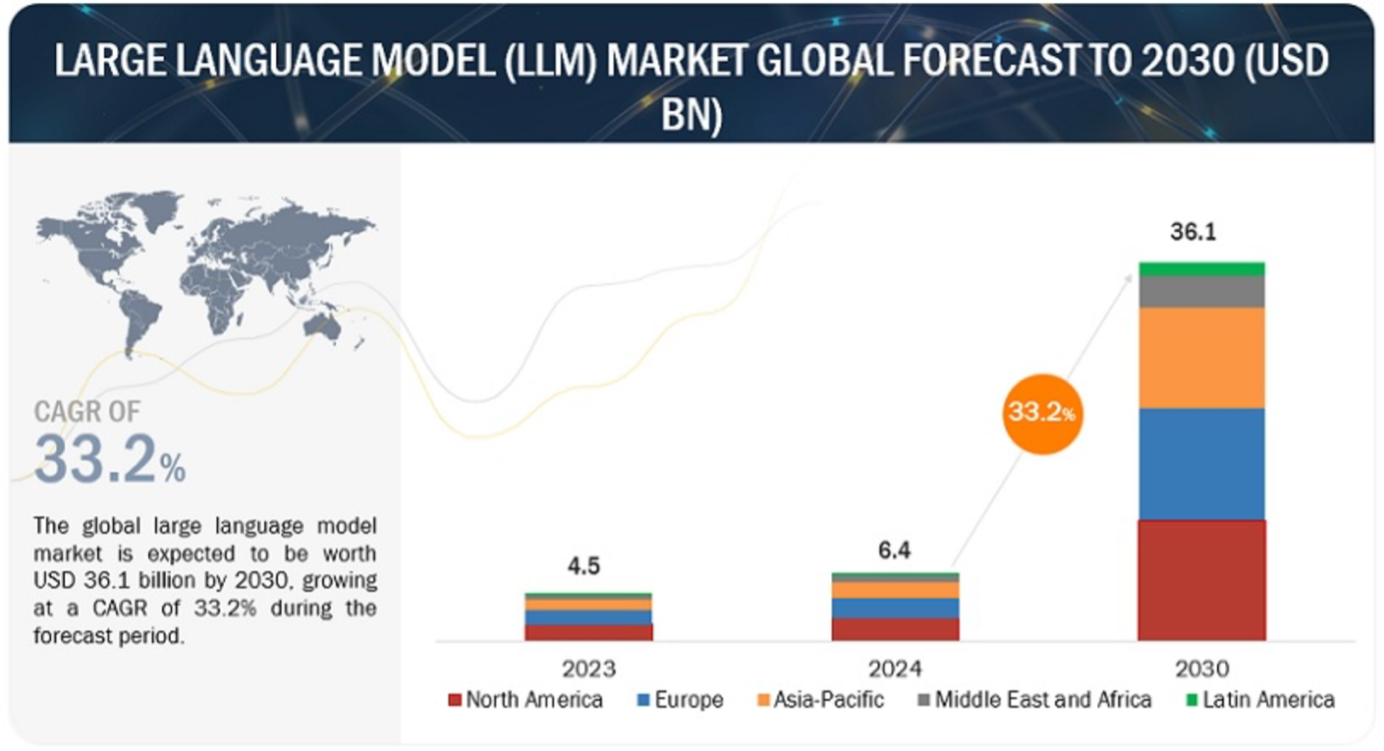
Market Growth Analysis and Dynamics
Market Expansion: Based on forecasts, the global market for Large Language Models (LLMs) is expected to experience dramatic growth, rising from $1,590.93 million USD in 2023 to an astounding $259,817.73 million USD by 2030. This exponential rise highlights how important LLMs are to a wide range of applications and sectors. Models in this parameter range are computationally possible and offer significant capabilities in a compromise between complexity and usefulness. This tendency is demonstrated by language models like LaMDA 2, GPT-3, BLOOMZ, Jurassic-2, and Falcon 180B, which demonstrate the potential of models in this size range to provide remarkable language generation and interpretation skills.
Accessibility of LLMs: One of the most promising aspects of large language models is their potential for widespread accessibility and global reach. Unlike many cutting-edge technologies that remain confined to well-funded labs or elite institutions, LLMs have a unique capacity to be democratized and made available to users around the world. With just an internet connection, individuals and organizations can access and leverage the immense capabilities of these language AI models through cloud APIs, open-source releases, and user-friendly interfaces. This accessibility allows developers, researchers, businesses, and creative professionals in every corner of the world to explore LLMs for a diverse array of applications - from educational tools to customer service chatbots to advanced content generation. Moreover, the multilingual abilities of many LLMs allow them to cater to populations speaking a wide variety of languages, further amplifying their global relevance.
Enterprise Adoption: As large language models continue to demonstrate their capabilities across a wide range of natural language processing tasks, their adoption within enterprises is accelerating rapidly. Businesses are recognizing the immense potential of LLMs to drive operational efficiencies, enhance customer experiences, and unlock new revenue streams. From automating customer service interactions and generating marketing content to summarizing dense documents and extracting insights from vast data repositories, LLMs are being leveraged across various departments and functions within organizations.
Technology giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon have already integrated LLM capabilities into their product suites, while numerous start-ups are building innovative LLM-powered solutions tailored for specific industries.
Industry Trends for Large Language Models
Prospects
- The growing need for LLMs in knowledge management and discovery.
- Improved language localization and translation.
- Using LLMs for Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Recognition.
Drivers
- Increased requirement for Content Creation and Curation Automation.
- Developments in Algorithms for Deep Learning.
- Improved Human-Machine communication is necessary.
- Increased accessibility of Big Datasets.
Limitations
- Exorbitant prices for inference optimization and model training.
- Less transparency in explainability and interpretability.
- Biases in data and quality issues.
Technology Roadmaps for LLM
Short Term (1-5 years) :
- Continuous learning to add new information to the models.
- Robust alignment and control techniques.
- Unsupervised multitask learning across diverse tasks.
- Tailored hardware accelerators that allow models with trillion parameters.
- On-device LLM deployments for edge computing and privacy.
Long Term (5+ years) :
- Robust reasoning abilities and real-world knowledge grounded in common sense.
- Emergent linguistic competencies that transcend the bounds of the training data.
- Language comprehension and generation reaching parity with human-level performance.
- Open-domain conversational AI assistants with versatile and unconstrained dialogue skills.
- Integrated multimodal models that seamlessly combine language, visual, and auditory modalities.
Key Market Players
The market for artificial intelligence and large language models is dominated by major tech giants as well as several ambitious startups. Companies like Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Meta, and Apple are pioneering research into LLMs and integrating them into their product offerings. Google's LaMDA and PaLM, Microsoft's Turing Models, and Meta's LLaMA are just some examples.
OpenAI, with its GPT series including the renowned GPT-3, has been a leader and catalyzing force. Anthropic's Constitutional AI and DeepMind's Chinchilla illustrate the innovative work happening at AI-first companies. Traditional tech leaders like IBM (with its Watson platform) and NVIDIA (powering LLM training with GPUs) also play key roles. Numerous startups like Adept, Cohere, Jasper, and Anthropic are laser-focused on commercializing LLMs across verticals. Governments globally are funding LLM research as the technology has widespread economic and strategic implications.
With rapid advances and immense investment, the competitive landscape for generative AI remains dynamic, as players race to develop the most capable and responsible LLMs.
Conclusion
As large language models continue their rapid evolution, driven by unprecedented computational scale and vast datasets, their impact across industries is set to intensify. While grappling with challenges around safety, bias, and ethical deployment remains crucial, the opportunities presented by LLMs are too transformative to ignore. The market landscape, while still nascent, is rife with innovation and competition as tech titans and ambitious startups race to develop the most advanced and responsible LLMs.
Ultimately, the mainstreaming of LLMs appears inevitable, poised to redefine productivity, augment human intelligence, and unlock new frontiers in our increasingly digital and language-driven world. The era of large language models is here, and its transformative impact will reverberate across industries and societies for years to come.





