How Gen AI is Disrupting Marketing Science & What You Need to Know
“Despite evidence that leadership in disruptive innovation pays such huge dividends, established firms, often fail to take the lead.” - Clayton Christensen, Innovator’s Dilemma

Summary:
McKinsey reported that Gen AI features stand to add up to $4.4 trillion to the global economy, annually [1]. While, Goldman Sachs predicts a 7% or nearly $7 trillion—increase in global GDP attributable to generative AI and lift in productivity growth by 1.5 percentage points over a 10-year period [2]. Gen AI could lead to an increase in productivity of marketing between 5 and 15 percent of total marketing spend, worth about $463 billion annually [3]. The world is rapidly changing, and companies that sit on the sidelines risk being left behind!
In this blog, I have presented the evolution of Gen AI and how Gen AI is fostering disruptive innovation in the world of marketing science. The purpose of this blog is to provide food for thought to leaders and practitioners of AI and Marketing Science.
Introduction - Rise of Gen AI
Technically, generative AI (Gen AI) can be defined as deep neural networks pre-trained on vast datasets to create a foundation model, which is then fine-tuned to generate new content based on human instructions. Gen AI represents a shift toward self-supervised machine learning, marking a departure from the supervised learning methods that dominated earlier AI developments [9].
In supervised learning, machines are trained by comparing their outputs to correct answers provided in the form of "labels" or "annotations," which require significant human effort in labour-intensive tasks. In contrast, self-supervised learning eliminates the need for annotated datasets. Instead, the model is trained by removing parts of the data and tasking it with "predicting" the missing elements. In essence, self-supervised learning derives supervisory signals directly from the data itself, often leveraging its inherent structure. This approach has the potential to unlock what is referred to as the "dark matter of intelligence" by Yann LeCun and Ishan Misra from Meta [4].
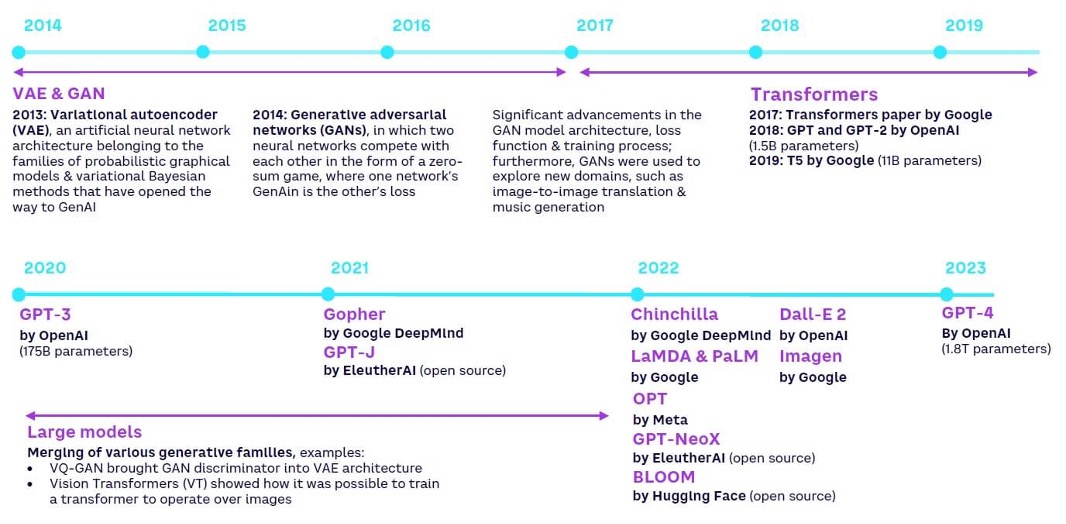
Figure 1: Evolution of Gen AI [10]
The adoption of self-supervised learning, combined with advancements in computing power (e.g., GPUs) and the introduction of the Transformer architecture (Vaswani et al., 2017), which enables faster and more efficient training, has led to the development of foundation models such as BERT, RoBERTa, BART, and T5. A foundation model is a large, pre-trained model that serves as a base for creating more specialized, task-specific models [9]. These foundation models form the backbone of generative AI capabilities. Generative AI models are creative systems capable of producing new content—such as text, images, and videos—by leveraging patterns learned during training to predict the next element in a sequence. Figure 1 illustrates the evolution of generative AI, highlighting the exponential growth in the number of parameters trained: GPT-2 (1.5 billion) → T5 by Google (11 billion) → GPT-3 (175 billion) → GPT-4 (1.8 trillion).
Disrupting Marketing Science
Paola Cillo et al. [6] conducted research involving managers from various industries, including high-end fashion, fast-moving consumer goods, insurance, and utilities. Their findings suggest that the repeated use of generative AI will significantly transform marketing capabilities, potentially rendering some obsolete or less valuable. Additionally, they anticipate that widespread adoption of generative AI will lead to shifts in consumer skills and preferences as a broader societal impact.
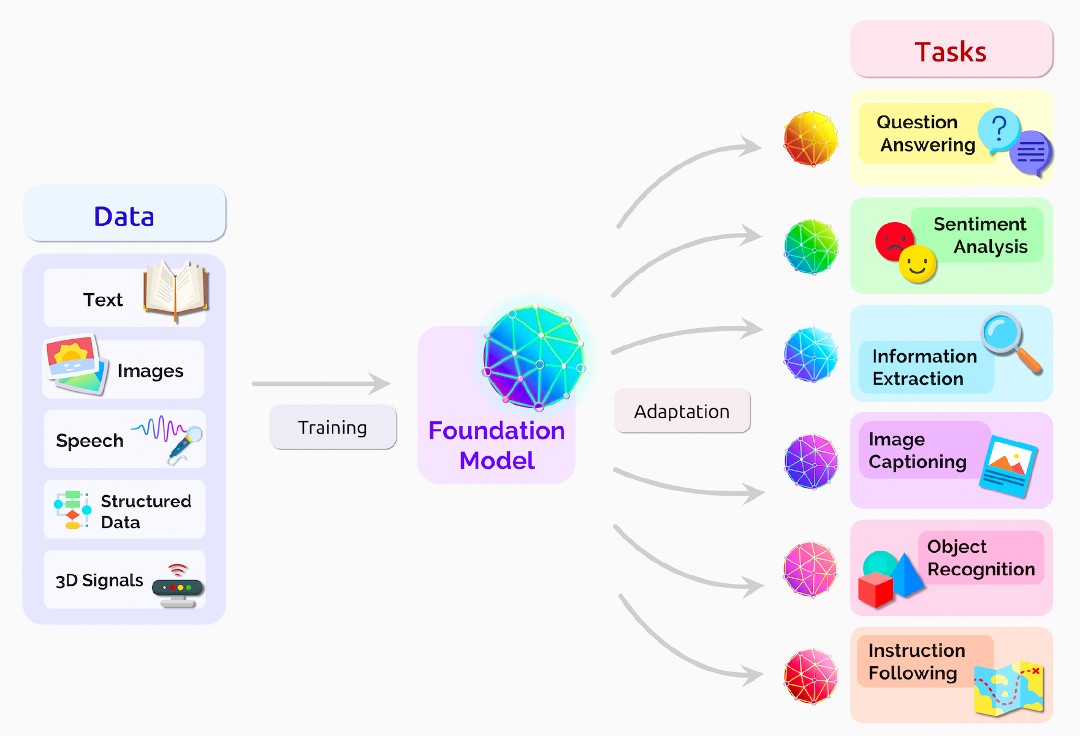
Figure 2: Uses of Gen AI across tasks [9]
Following are some areas in consumer marketing where Gen AI could be used as per MIT Technology Review [5]. Most innovator or early adopter companies like Rakuten, are already using Gen AI for these use cases:
Optimizing pricing strategies
Understanding user preferences, behaviours and contextual cues
Developing personalized marketing
Increasing precision and effectiveness of ad targeting
Emergent Capabilities of Gen AI [5] in Marketing Science:
-
Generating ideas for new products:
The rapid generation of response-ready product concepts through gen AI can enhance the efficiency of successful product development, improve testing accuracy, and accelerate time to market. Research by Lennart Meincke et al. [7] found that generative AI produces ideas that elicit higher purchase intentions from potential consumers. Their findings highlight that, despite certain limitations, AI-driven creativity offers significant advantages in generating high-quality ideas for new product development. For example, Mattel leverages AI in its Hot Wheels product development process to create four times as many product concept images as before, inspiring innovative features and designs. Similarly, Kellogg’s uses AI to analyse trending recipes that include (or could include) breakfast cereal, using the insights to launch social campaigns featuring creative and relevant recipes. Meanwhile, L’Oréal employs AI to analyse millions of online comments, images, and videos to uncover opportunities for product innovation. -
Personalization of Marketing Campaigns:
Crafts retailer Michaels Stores is leveraging generative AI to enhance customer engagement through more personalized and frequent interactions with its shoppers. The company developed a content generation and decision-making platform to streamline copy creation and gain deeper insights into how different customer segments respond to various messages. As a result, Michaels has increased the personalization of its email campaigns from 20 percent to 95 percent, leading to a 41 percent increase in click-through rates for SMS campaigns and a 25 percent increase for email campaigns. -
Consumer Behaviour Analysis:
Hyper-personalization efforts are further enhanced by more detailed analyses of consumer behavior, which can be significantly improved with the help of generative AI. For instance, personal clothing service Stitch Fix utilizes generative AI to assist stylists in interpreting customer feedback and making tailored product recommendations. Similarly, Instacart employs generative AI to provide customers with personalized recipes, meal-planning suggestions, and automatically generated shopping lists.

How Generative AI Can Augment Human Creativity [8]

Image generated using OpenArt.ai
Risks, Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Risks - Moore’s Chasm
Moore’s Chasm looms between Early Adopters and the Early Majority. Lots of technological innovations that are tried by Early Adopters fail to gain sufficient acceptance to pass the criteria of the Early Majority.
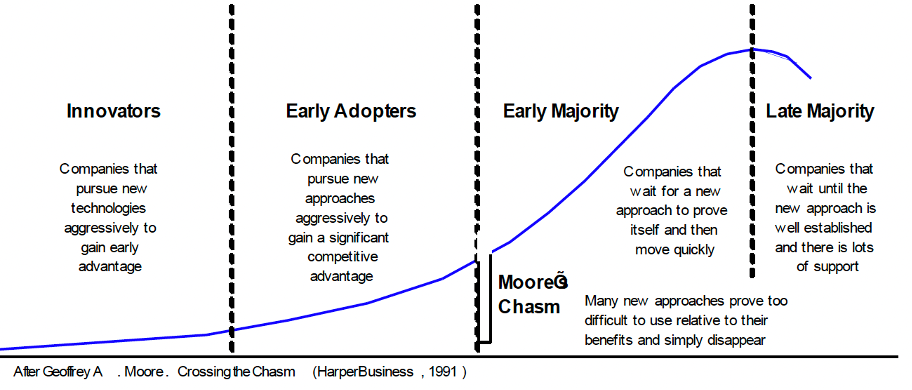
Figure 3: Moore’s technology adoption lifecycle curve
"Disruptive innovations generate what the Gartner Group has called a Hype Cycle, which begins with a peak of inflated expectations, followed by a trough of disillusionment, followed by more slowly developing sustained adoption and value creation. In this context, AI, and specifically Generative AI, is at a peak of inflated expectations. That said, the ease of which it can be integrated into the existing workflows, plus the astounding amount of risk capital that has been deployed to accelerate training the Large Language Models, portends a much faster adoption rate than normal, one more like the Apple iPhone, less like The World Wide Web” - Geoffrey Moore author of Crossing the Chasm
The Hype Cycle for AI (figure 4) shows that Gen AI has already crossed the peak of inflated expectations. Companies which fail to adopt Gen AI and wait for Moore’s Chasm, risk losing their competitive advantage and eventually market share.
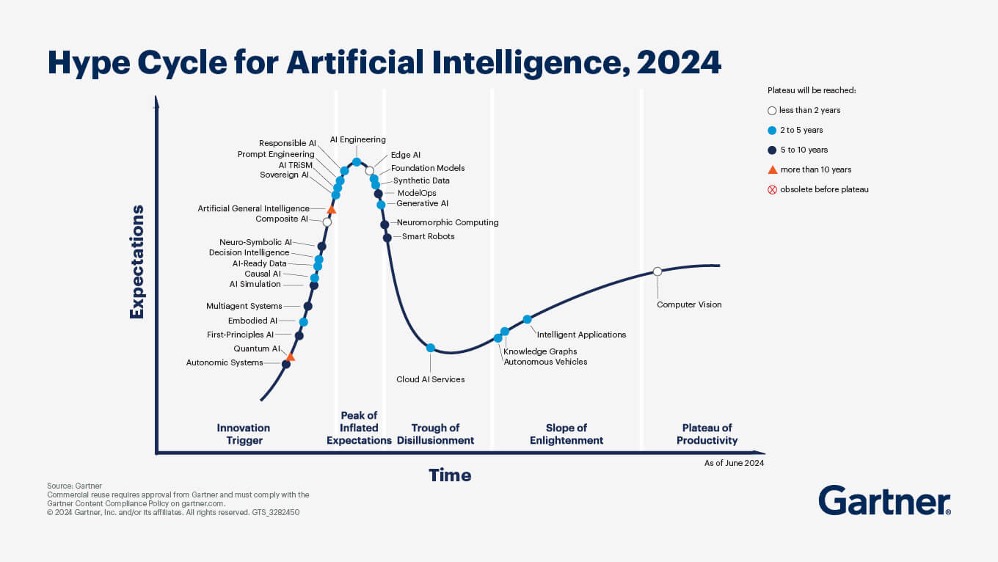
Figure 4: Hype Cycle for AI ‘24 shows that Gen AI has crossed the peak of inflated expectations [12]
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Gen AI comes with governance challenges that may exceed the capabilities of existing data governance frameworks. When working with generative models that absorb and regurgitate all the data they are exposed to, without regard for its sensitivity, organizations must attend to security and privacy in a new way. Enterprises also now must manage exponentially growing data sources and data that is machine-generated or of questionable provenance, requiring a unified and consistent governance approach. And lawmakers and regulators have grown conscious of generative AI’s risks, as well, leading to legal cases, usage restrictions, and new regulations, such as the European Union’s AI Act. [5]
Conclusion
One of the biggest opportunities generative AI offers to businesses and governments is to augment human creativity and overcome the challenges of democratizing innovation [8]. Although we are still in the early stages and the future of generative AI remains uncertain, it is clear that a generative AI-driven transformation is on the horizon. Here’s how companies can take the first steps to ensure they stay ahead of the curve:
-
Spinning Off an Independent Organization: Established firms that successfully built a strong market position in a disruptive technology were those that spun off from the mainstream company an independent, autonomously operated organization. Quantum, Control Data, IBM’s PC Division, Allen Bradley, and Hewlett-Packard’s desk-jet initiative all succeeded because they created organizations whose survival was predicated upon successful commercialization of the disruptive technology: These firms embedded a dedicated organization squarely within the emerging value network. [11]
-
Fail Fast, Succeed Faster: For high-priority, low-complexity use cases where off-the-shelf generative AI tools can be utilized, initiate a few pilot projects to explore how generative AI can deliver value. These efforts should help identify the required talent and skills to sustain this capability, as well as the operating model needed for effective scaling. A brief design can outline the user value proposition and specific use case, while a build plan can detail the technical requirements, prototypes, and decisions around whether to build, buy, or partner for implementation. [3]
References
https://ai.meta.com/blog/self-supervised-learning-the-dark-matter-of-intelligence/
Cillo, Paola, and Gaia Rubera. "Generative AI in innovation and marketing processes: A roadmap of research opportunities." Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science(2024): 1-18.
Meincke, Lennart and Girotra, Karan and Nave, Gideon and Terwiesch, Christian and Ulrich, Karl T., Using Large Language Models for Idea Generation in Innovation (September 07, 2024). The Wharton School Research Paper Forthcoming, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4526071 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4526071
https://hbr.org/2023/07/how-generative-ai-can-augment-human-creativity
Bommasani, Rishi, Drew A. Hudson, Ehsan Adeli, Russ Altman, Simran Arora, Sydney von Arx, Michael S. Bernstein et al. "On the opportunities and risks of foundation models." arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.07258 (2021).
Christensen, Clayton M. The Innovator's Dilemma. Harvard Business Review Press, 2016.
https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/hype-cycle-for-artificial-intelligence





